Camera Viewing Geometry
First, we'll keep the rays coming from the origin and heading to the \( z = -1\) plane. We could make it the \( z = -2 \) plane, or whatever, as long as we made ℎ a ratio to that distance. Here is our setup:
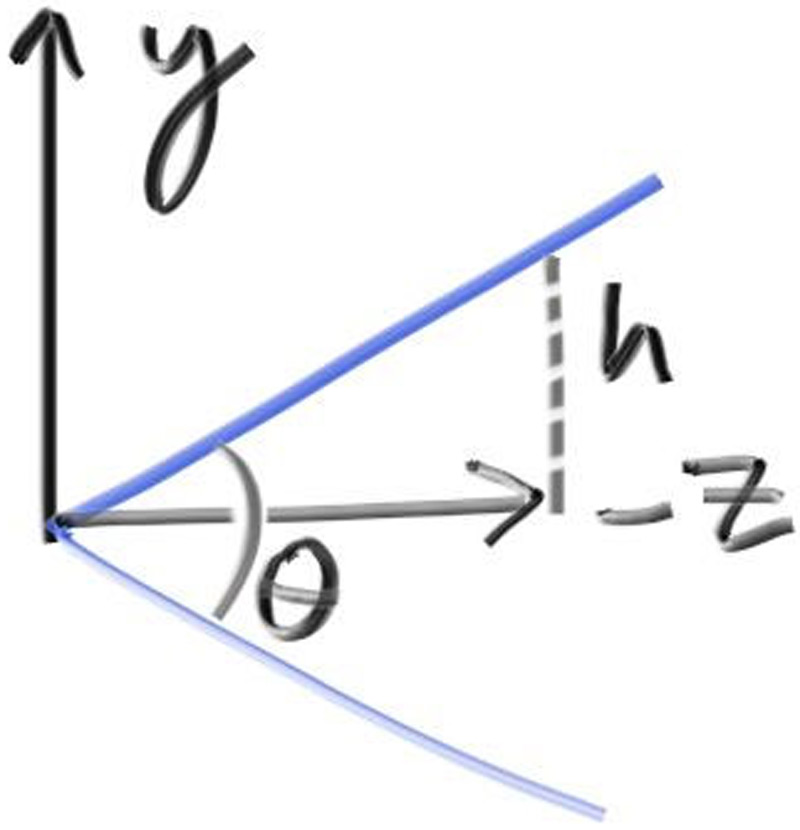
Figure 18: Camera viewing geometry (from the side)
This implies \( h = \tan (\frac{\theta}{2}) \). Our camera now becomes:
diff --git a/src/camera.rs b/src/camera.rs
index 1927898..8e256aa 100644
--- a/src/camera.rs
+++ b/src/camera.rs
@@ -1,168 +1,179 @@
use crate::{hittable::Hittable, prelude::*};
pub struct Camera {
/// Ratio of image width over height
pub aspect_ratio: f64,
/// Rendered image width in pixel count
pub image_width: i32,
// Count of random samples for each pixel
pub samples_per_pixel: i32,
// Maximum number of ray bounces into scene
pub max_depth: i32,
+ // Vertical view angle (field of view)
+ pub vfov: f64,
/// Rendered image height
image_height: i32,
// Color scale factor for a sum of pixel samples
pixel_samples_scale: f64,
/// Camera center
center: Point3,
/// Location of pixel 0, 0
pixel00_loc: Point3,
/// Offset to pixel to the right
pixel_delta_u: Vec3,
/// Offset to pixel below
pixel_delta_v: Vec3,
}
impl Default for Camera {
fn default() -> Self {
Self {
aspect_ratio: 1.0,
image_width: 100,
samples_per_pixel: 10,
max_depth: 10,
+ vfov: 90.0,
image_height: Default::default(),
pixel_samples_scale: Default::default(),
center: Default::default(),
pixel00_loc: Default::default(),
pixel_delta_u: Default::default(),
pixel_delta_v: Default::default(),
}
}
}
impl Camera {
pub fn with_aspect_ratio(mut self, aspect_ratio: f64) -> Self {
self.aspect_ratio = aspect_ratio;
self
}
pub fn with_image_width(mut self, image_width: i32) -> Self {
self.image_width = image_width;
self
}
pub fn with_samples_per_pixel(mut self, samples_per_pixel: i32) -> Self {
self.samples_per_pixel = samples_per_pixel;
self
}
pub fn with_max_depth(mut self, max_depth: i32) -> Self {
self.max_depth = max_depth;
self
}
+ pub fn with_vfov(mut self, vfov: f64) -> Self {
+ self.vfov = vfov;
+
+ self
+ }
+
pub fn render(&mut self, world: &impl Hittable) -> std::io::Result<()> {
self.initialize();
println!("P3");
println!("{} {}", self.image_width, self.image_height);
println!("255");
for j in 0..self.image_height {
info!("Scanlines remaining: {}", self.image_height - j);
for i in 0..self.image_width {
let mut pixel_color = Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for _sample in 0..self.samples_per_pixel {
let r = self.get_ray(i, j);
pixel_color += Self::ray_color(r, self.max_depth, world);
}
write_color(std::io::stdout(), self.pixel_samples_scale * pixel_color)?;
}
}
info!("Done.");
Ok(())
}
fn initialize(&mut self) {
self.image_height = {
let image_height = (self.image_width as f64 / self.aspect_ratio) as i32;
if image_height < 1 { 1 } else { image_height }
};
self.pixel_samples_scale = 1.0 / self.samples_per_pixel as f64;
self.center = Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// Determine viewport dimensions.
let focal_length = 1.0;
- let viewport_height = 2.0;
+ let theta = self.vfov.to_radians();
+ let h = f64::tan(theta / 2.0);
+ let viewport_height = 2.0 * h * focal_length;
let viewport_width =
viewport_height * (self.image_width as f64) / (self.image_height as f64);
// Calculate the vectors across the horizontal and down the vertical viewport edges.
let viewport_u = Vec3::new(viewport_width, 0.0, 0.0);
let viewport_v = Vec3::new(0.0, -viewport_height, 0.0);
// Calculate the horizontal and vertical delta vectors from pixel to pixel.
self.pixel_delta_u = viewport_u / self.image_width as f64;
self.pixel_delta_v = viewport_v / self.image_height as f64;
// Calculate the location of the upper left pixel.
let viewport_upper_left =
self.center - Vec3::new(0.0, 0.0, focal_length) - viewport_u / 2.0 - viewport_v / 2.0;
self.pixel00_loc = viewport_upper_left + 0.5 * (self.pixel_delta_u + self.pixel_delta_v);
}
fn get_ray(&self, i: i32, j: i32) -> Ray {
// Construct a camera ray originating from the origin and directed at randomly sampled
// point around the pixel location i, j.
let offset = Self::sample_square();
let pixel_sample = self.pixel00_loc
+ ((i as f64 + offset.x()) * self.pixel_delta_u)
+ ((j as f64 + offset.y()) * self.pixel_delta_v);
let ray_origin = self.center;
let ray_direction = pixel_sample - ray_origin;
Ray::new(ray_origin, ray_direction)
}
fn sample_square() -> Vec3 {
// Returns the vector to a random point in the [-.5,-.5]-[+.5,+.5] unit square.
Vec3::new(
rand::random::<f64>() - 0.5,
rand::random::<f64>() - 0.5,
0.0,
)
}
fn _sample_disk(radius: f64) -> Vec3 {
// Returns a random point in the unit (radius 0.5) disk centered at the origin.
radius * random_in_unit_disk()
}
fn ray_color(r: Ray, depth: i32, world: &impl Hittable) -> Color {
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered.
if depth <= 0 {
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if let Some(rec) = world.hit(r, Interval::new(0.001, INFINITY)) {
if let Some((scattered, attenuation)) = rec.mat.scatter(r, rec.clone()) {
return attenuation * Self::ray_color(scattered, depth - 1, world);
}
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction());
let a = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y() + 1.0);
(1.0 - a) * Color::new(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + a * Color::new(0.5, 0.7, 1.0)
}
}Listing 80: [camera.rs] Camera with adjustable field-of-view (fov)
We'll test out these changes with a simple scene of two touching spheres, using a 90° field of view.
diff --git a/src/main.rs b/src/main.rs
index c0d6703..e906c8c 100644
--- a/src/main.rs
+++ b/src/main.rs
@@ -1,52 +1,37 @@
use code::{
camera::Camera,
hittable_list::HittableList,
material::{Dielectric, Lambertian, Metal},
prelude::*,
sphere::Sphere,
};
fn main() -> std::io::Result<()> {
let mut world = HittableList::new();
- let material_ground = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.8, 0.8, 0.0)));
- let material_center = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.1, 0.2, 0.5)));
- let material_left = Rc::new(Dielectric::new(1.5));
- let material_bubble = Rc::new(Dielectric::new(1.0 / 1.5));
- let material_right = Rc::new(Metal::new(Color::new(0.8, 0.6, 0.2), 1.0));
+ let r = f64::cos(PI / 4.0);
+
+ let material_left = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)));
+ let material_right = Rc::new(Lambertian::new(Color::new(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)));
world.add(Rc::new(Sphere::new(
- Point3::new(0.0, -100.5, -1.0),
- 100.0,
- material_ground,
- )));
- world.add(Rc::new(Sphere::new(
- Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, -1.2),
- 0.5,
- material_center,
- )));
- world.add(Rc::new(Sphere::new(
- Point3::new(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
- 0.5,
+ Point3::new(-r, 0.0, -1.0),
+ r,
material_left,
)));
world.add(Rc::new(Sphere::new(
- Point3::new(-1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
- 0.4,
- material_bubble,
- )));
- world.add(Rc::new(Sphere::new(
- Point3::new(1.0, 0.0, -1.0),
- 0.5,
+ Point3::new(r, 0.0, -1.0),
+ r,
material_right,
)));
env_logger::init();
Camera::default()
.with_aspect_ratio(16.0 / 9.0)
.with_image_width(400)
.with_samples_per_pixel(100)
.with_max_depth(50)
+ .with_vfov(90.0)
.render(&world)
}Listing 81: [main.rs] Scene with wide-angle camera
This gives us the rendering:
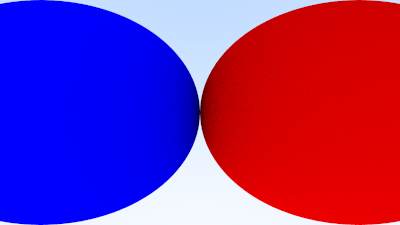
Image 19: A wide-angle view