Mirrored Light Reflection
For polished metals the ray won’t be randomly scattered. The key question is: How does a ray get reflected from a metal mirror? Vector math is our friend here:
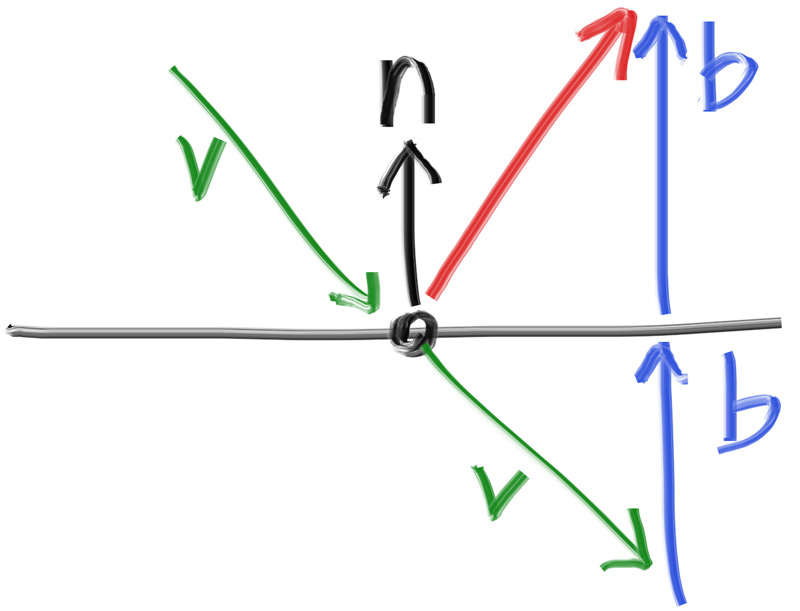
Figure 15: Ray reflection
The reflected ray direction in red is just \( \mathbf{v} + 2 \mathbf{b} \). In our design, \( \mathbf{n} \) is a unit vector (length one), but \( \mathbf{v} \) may not be. To get the vector \( \mathbf{b} \), we scale the normal vector by the length of the projection of \( \mathbf{v} \) onto \( \mathbf{n} \), which is given by the dot product \( \mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{n} \). (If \( \mathbf{n} \) were not a unit vector, we would also need to divide this dot product by the length of \( \mathbf{n} \).) Finally, because \( \mathbf{b} \) points into the surface, and we want \( \mathbf{b} \) to point out of the surface, we need to negate this projection length.
Putting everything together, we get the following computation of the reflected vector:
diff --git a/src/vec3.rs b/src/vec3.rs
index 3348fef..4cb0b6f 100644
--- a/src/vec3.rs
+++ b/src/vec3.rs
@@ -1,229 +1,234 @@
use std::{
fmt::Display,
ops::{Add, AddAssign, Div, DivAssign, Index, IndexMut, Mul, MulAssign, Neg, Sub},
};
#[derive(Debug, Default, Clone, Copy)]
pub struct Vec3 {
pub e: [f64; 3],
}
pub type Point3 = Vec3;
impl Vec3 {
pub fn new(e0: f64, e1: f64, e2: f64) -> Self {
Self { e: [e0, e1, e2] }
}
pub fn x(&self) -> f64 {
self.e[0]
}
pub fn y(&self) -> f64 {
self.e[1]
}
pub fn z(&self) -> f64 {
self.e[2]
}
pub fn length(&self) -> f64 {
f64::sqrt(self.length_squared())
}
pub fn length_squared(&self) -> f64 {
self.e[0] * self.e[0] + self.e[1] * self.e[1] + self.e[2] * self.e[2]
}
pub fn near_zero(&self) -> bool {
// Return true if the vector is close to zero in all dimensions.
const S: f64 = 1e-8;
self.e[0].abs() < S && self.e[1].abs() < S && self.e[2].abs() < S
}
pub fn random() -> Self {
Vec3 { e: rand::random() }
}
pub fn random_range(min: f64, max: f64) -> Self {
Vec3::new(
rand::random_range(min..max),
rand::random_range(min..max),
rand::random_range(min..max),
)
}
}
impl Neg for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn neg(self) -> Self::Output {
Self::Output {
e: self.e.map(|e| -e),
}
}
}
impl Index<usize> for Vec3 {
type Output = f64;
fn index(&self, index: usize) -> &Self::Output {
&self.e[index]
}
}
impl IndexMut<usize> for Vec3 {
fn index_mut(&mut self, index: usize) -> &mut Self::Output {
&mut self.e[index]
}
}
impl AddAssign for Vec3 {
fn add_assign(&mut self, rhs: Self) {
self.e[0] += rhs.e[0];
self.e[1] += rhs.e[1];
self.e[2] += rhs.e[2];
}
}
impl MulAssign<f64> for Vec3 {
fn mul_assign(&mut self, rhs: f64) {
self.e[0] *= rhs;
self.e[1] *= rhs;
self.e[2] *= rhs;
}
}
impl DivAssign<f64> for Vec3 {
fn div_assign(&mut self, rhs: f64) {
self.mul_assign(1.0 / rhs);
}
}
impl Display for Vec3 {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut std::fmt::Formatter<'_>) -> std::fmt::Result {
write!(f, "{} {} {}", self.e[0], self.e[1], self.e[2])
}
}
impl Add for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn add(self, rhs: Self) -> Self::Output {
Self::Output {
e: [
self.e[0] + rhs.e[0],
self.e[1] + rhs.e[1],
self.e[2] + rhs.e[2],
],
}
}
}
impl Sub for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn sub(self, rhs: Self) -> Self::Output {
Self::Output {
e: [
self.e[0] - rhs.e[0],
self.e[1] - rhs.e[1],
self.e[2] - rhs.e[2],
],
}
}
}
impl Mul for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn mul(self, rhs: Self) -> Self::Output {
Self::Output {
e: [
self.e[0] * rhs.e[0],
self.e[1] * rhs.e[1],
self.e[2] * rhs.e[2],
],
}
}
}
impl Mul<f64> for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn mul(self, rhs: f64) -> Self::Output {
Self::Output {
e: [self.e[0] * rhs, self.e[1] * rhs, self.e[2] * rhs],
}
}
}
impl Mul<Vec3> for f64 {
type Output = Vec3;
fn mul(self, rhs: Vec3) -> Self::Output {
rhs.mul(self)
}
}
impl Div<f64> for Vec3 {
type Output = Self;
fn div(self, rhs: f64) -> Self::Output {
self * (1.0 / rhs)
}
}
#[inline]
pub fn dot(u: Vec3, v: Vec3) -> f64 {
u.e[0] * v.e[0] + u.e[1] * v.e[1] + u.e[2] * v.e[2]
}
#[inline]
pub fn cross(u: Vec3, v: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
Vec3::new(
u.e[1] * v.e[2] - u.e[2] * v.e[1],
u.e[2] * v.e[0] - u.e[0] * v.e[2],
u.e[0] * v.e[1] - u.e[1] * v.e[0],
)
}
#[inline]
pub fn unit_vector(v: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
v / v.length()
}
#[inline]
pub fn random_unit_vector() -> Vec3 {
loop {
let p = Vec3::random_range(-1.0, 1.0);
let lensq = p.length_squared();
if 1e-160 < lensq && lensq <= 1.0 {
return p / f64::sqrt(lensq);
}
}
}
#[inline]
pub fn random_on_hemisphere(normal: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
let on_unit_sphere = random_unit_vector();
if dot(on_unit_sphere, normal) > 0.0 {
on_unit_sphere
} else {
-on_unit_sphere
}
}
#[inline]
+pub fn reflect(v: Vec3, n: Vec3) -> Vec3 {
+ v - 2.0 * dot(v, n) * n
+}
+
+#[inline]
pub fn random_in_unit_disk() -> Vec3 {
loop {
let p = Vec3::new(
rand::random_range(-1.0..1.0),
rand::random_range(-1.0..1.0),
0.0,
);
if p.length_squared() < 1.0 {
return p;
}
}
}Listing 64: [vec3.rs] vec3 reflection function
The metal material just reflects rays using that formula:
diff --git a/src/material.rs b/src/material.rs
index 1b49e15..8475d17 100644
--- a/src/material.rs
+++ b/src/material.rs
@@ -1,34 +1,55 @@
use crate::{hittable::HitRecord, prelude::*};
pub trait Material {
fn scatter(&self, _r_in: Ray, _rec: HitRecord) -> Option<(Ray, Color)> {
None
}
}
#[derive(Debug, Default, Clone, Copy)]
pub struct Lambertian {
albedo: Color,
}
impl Lambertian {
pub fn new(albedo: Color) -> Self {
Self { albedo }
}
}
impl Material for Lambertian {
fn scatter(&self, _r_in: Ray, rec: HitRecord) -> Option<(Ray, Color)> {
let mut scatter_direction = rec.normal + random_unit_vector();
// Catch degenerate scatter direction
if scatter_direction.near_zero() {
scatter_direction = rec.normal;
}
let scattered = Ray::new(rec.p, scatter_direction);
let attenuation = self.albedo;
Some((scattered, attenuation))
}
}
+
+#[derive(Debug, Default, Clone, Copy)]
+pub struct Metal {
+ albedo: Color,
+}
+
+impl Metal {
+ pub fn new(albedo: Color) -> Self {
+ Self { albedo }
+ }
+}
+
+impl Material for Metal {
+ fn scatter(&self, r_in: Ray, rec: HitRecord) -> Option<(Ray, Color)> {
+ let reflected = reflect(r_in.direction(), rec.normal);
+ let scattered = Ray::new(rec.p, reflected);
+ let attenuation = self.albedo;
+
+ Some((scattered, attenuation))
+ }
+}Listing 65: [material.rs] Metal material with reflectance function
We need to modify the ray_color() function for all of our changes:
diff --git a/src/camera.rs b/src/camera.rs
index e6c60c3..1927898 100644
--- a/src/camera.rs
+++ b/src/camera.rs
@@ -1,166 +1,168 @@
use crate::{hittable::Hittable, prelude::*};
pub struct Camera {
/// Ratio of image width over height
pub aspect_ratio: f64,
/// Rendered image width in pixel count
pub image_width: i32,
// Count of random samples for each pixel
pub samples_per_pixel: i32,
// Maximum number of ray bounces into scene
pub max_depth: i32,
/// Rendered image height
image_height: i32,
// Color scale factor for a sum of pixel samples
pixel_samples_scale: f64,
/// Camera center
center: Point3,
/// Location of pixel 0, 0
pixel00_loc: Point3,
/// Offset to pixel to the right
pixel_delta_u: Vec3,
/// Offset to pixel below
pixel_delta_v: Vec3,
}
impl Default for Camera {
fn default() -> Self {
Self {
aspect_ratio: 1.0,
image_width: 100,
samples_per_pixel: 10,
max_depth: 10,
image_height: Default::default(),
pixel_samples_scale: Default::default(),
center: Default::default(),
pixel00_loc: Default::default(),
pixel_delta_u: Default::default(),
pixel_delta_v: Default::default(),
}
}
}
impl Camera {
pub fn with_aspect_ratio(mut self, aspect_ratio: f64) -> Self {
self.aspect_ratio = aspect_ratio;
self
}
pub fn with_image_width(mut self, image_width: i32) -> Self {
self.image_width = image_width;
self
}
pub fn with_samples_per_pixel(mut self, samples_per_pixel: i32) -> Self {
self.samples_per_pixel = samples_per_pixel;
self
}
pub fn with_max_depth(mut self, max_depth: i32) -> Self {
self.max_depth = max_depth;
self
}
pub fn render(&mut self, world: &impl Hittable) -> std::io::Result<()> {
self.initialize();
println!("P3");
println!("{} {}", self.image_width, self.image_height);
println!("255");
for j in 0..self.image_height {
info!("Scanlines remaining: {}", self.image_height - j);
for i in 0..self.image_width {
let mut pixel_color = Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
for _sample in 0..self.samples_per_pixel {
let r = self.get_ray(i, j);
pixel_color += Self::ray_color(r, self.max_depth, world);
}
write_color(std::io::stdout(), self.pixel_samples_scale * pixel_color)?;
}
}
info!("Done.");
Ok(())
}
fn initialize(&mut self) {
self.image_height = {
let image_height = (self.image_width as f64 / self.aspect_ratio) as i32;
if image_height < 1 { 1 } else { image_height }
};
self.pixel_samples_scale = 1.0 / self.samples_per_pixel as f64;
self.center = Point3::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
// Determine viewport dimensions.
let focal_length = 1.0;
let viewport_height = 2.0;
let viewport_width =
viewport_height * (self.image_width as f64) / (self.image_height as f64);
// Calculate the vectors across the horizontal and down the vertical viewport edges.
let viewport_u = Vec3::new(viewport_width, 0.0, 0.0);
let viewport_v = Vec3::new(0.0, -viewport_height, 0.0);
// Calculate the horizontal and vertical delta vectors from pixel to pixel.
self.pixel_delta_u = viewport_u / self.image_width as f64;
self.pixel_delta_v = viewport_v / self.image_height as f64;
// Calculate the location of the upper left pixel.
let viewport_upper_left =
self.center - Vec3::new(0.0, 0.0, focal_length) - viewport_u / 2.0 - viewport_v / 2.0;
self.pixel00_loc = viewport_upper_left + 0.5 * (self.pixel_delta_u + self.pixel_delta_v);
}
fn get_ray(&self, i: i32, j: i32) -> Ray {
// Construct a camera ray originating from the origin and directed at randomly sampled
// point around the pixel location i, j.
let offset = Self::sample_square();
let pixel_sample = self.pixel00_loc
+ ((i as f64 + offset.x()) * self.pixel_delta_u)
+ ((j as f64 + offset.y()) * self.pixel_delta_v);
let ray_origin = self.center;
let ray_direction = pixel_sample - ray_origin;
Ray::new(ray_origin, ray_direction)
}
fn sample_square() -> Vec3 {
// Returns the vector to a random point in the [-.5,-.5]-[+.5,+.5] unit square.
Vec3::new(
rand::random::<f64>() - 0.5,
rand::random::<f64>() - 0.5,
0.0,
)
}
fn _sample_disk(radius: f64) -> Vec3 {
// Returns a random point in the unit (radius 0.5) disk centered at the origin.
radius * random_in_unit_disk()
}
fn ray_color(r: Ray, depth: i32, world: &impl Hittable) -> Color {
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered.
if depth <= 0 {
return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
if let Some(rec) = world.hit(r, Interval::new(0.001, INFINITY)) {
- let direction = rec.normal + random_unit_vector();
- return 0.1 * Self::ray_color(Ray::new(rec.p, direction), depth - 1, world);
+ if let Some((scattered, attenuation)) = rec.mat.scatter(r, rec.clone()) {
+ return attenuation * Self::ray_color(scattered, depth - 1, world);
+ }
+ return Color::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
let unit_direction = unit_vector(r.direction());
let a = 0.5 * (unit_direction.y() + 1.0);
(1.0 - a) * Color::new(1.0, 1.0, 1.0) + a * Color::new(0.5, 0.7, 1.0)
}
}Listing 66: [camera.rs] Ray color with scattered reflectance
Now we'll update the sphere constructor to initialize the material pointer mat:
diff --git a/src/sphere.rs b/src/sphere.rs
index 2b0026a..2a6b2ce 100644
--- a/src/sphere.rs
+++ b/src/sphere.rs
@@ -1,61 +1,60 @@
use crate::{
hittable::{HitRecord, Hittable},
- material::{Lambertian, Material},
+ material::Material,
prelude::*,
};
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct Sphere {
center: Point3,
radius: f64,
mat: Rc<dyn Material>,
}
impl Sphere {
- pub fn new(center: Point3, radius: f64) -> Self {
+ pub fn new(center: Point3, radius: f64, mat: Rc<dyn Material>) -> Self {
Self {
center,
radius: f64::max(0.0, radius),
- // TODO: Initialize the material pointer `mat`.
- mat: Rc::new(Lambertian::default()),
+ mat,
}
}
}
impl Hittable for Sphere {
fn hit(&self, r: Ray, ray_t: Interval) -> Option<HitRecord> {
let oc = self.center - r.origin();
let a = r.direction().length_squared();
let h = dot(r.direction(), oc);
let c = oc.length_squared() - self.radius * self.radius;
let discriminant = h * h - a * c;
if discriminant < 0.0 {
return None;
}
let sqrtd = f64::sqrt(discriminant);
// Find the nearest root that lies in the acceptable range.
let mut root = (h - sqrtd) / a;
if !ray_t.surrounds(root) {
root = (h + sqrtd) / a;
if !ray_t.surrounds(root) {
return None;
}
}
let t = root;
let p = r.at(t);
let mut rec = HitRecord {
t,
p,
mat: self.mat.clone(),
..Default::default()
};
let outward_normal = (p - self.center) / self.radius;
rec.set_face_normal(r, outward_normal);
Some(rec)
}
}Listing 67: [sphere.rs] Initializing sphere with a material